As AI matures and partner programs become more common, the gap between experimentation and effective execution is becoming clearer. Artificial intelligence has never been more promising — or more poorly executed.

Make Money With AI
Join our Partner Programs!
Boost your reputation, drive revenue and grow your business with CustomGPT.ai.
According to the McKinsey State of AI 2024 Report, only 23% of organizations have deployed AI across multiple business units, despite nearly 75% experimenting with it.
The gap isn’t caused by lack of tools — it’s caused by lack of clarity, alignment, and execution.
For marketing agencies, this shift presents both a challenge and an opportunity. AI can automate workflows, personalize campaigns, and uncover insights at scale — but only when implemented with discipline, structure, and a clear strategic roadmap.
When AI implementation for clients is done effectively, it becomes a powerful operational advantage, increasing ROI, speeding up decision-making, and enhancing the customer experience.
This roadmap gives agencies a practical, repeatable framework for scoping, planning, and deploying AI solutions for clients — from discovery to continuous improvement.
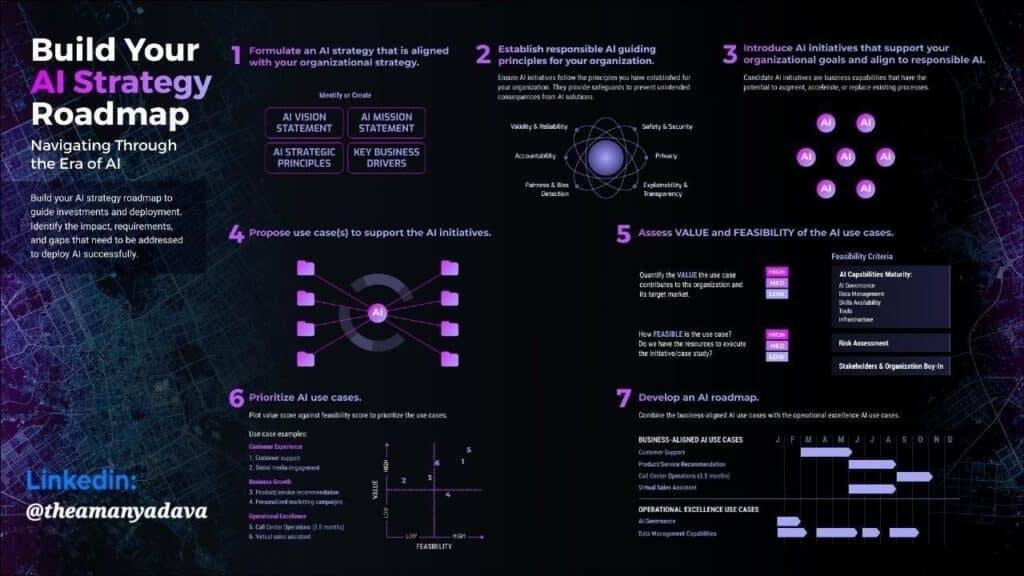
PHASE 1: Discovery & Scoping
Discovery lays the foundation for your entire AI project. This phase ensures that the right problem is being solved, the right people are involved, and the right use cases are prioritized.
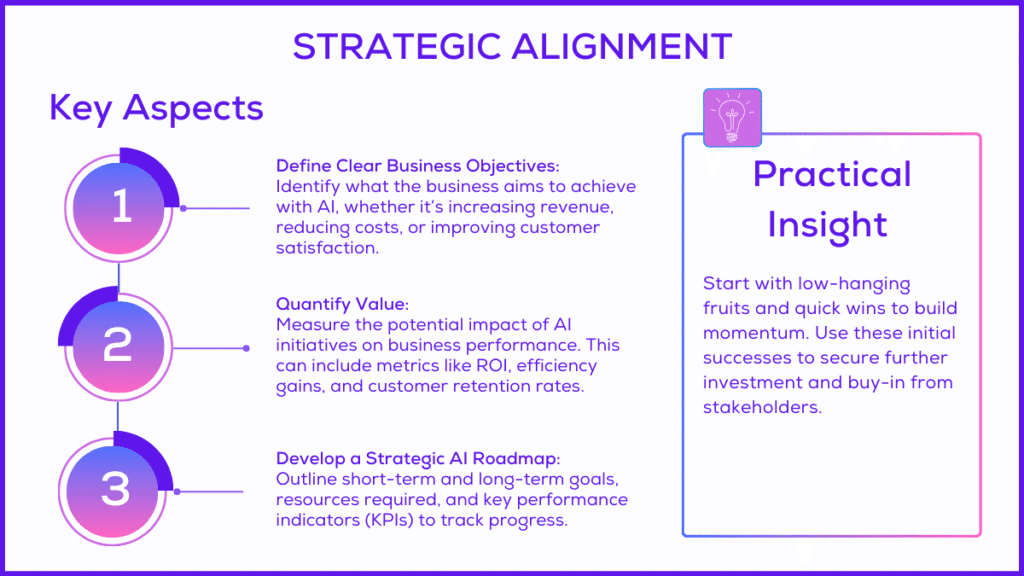
Identifying Business Objectives (Defining the Purpose of AI)
Clear business objectives ensure AI solves a meaningful problem rather than becoming a technical experiment. Agencies should help clients connect AI opportunities directly to measurable KPIs such as churn, ROAS, conversion rates, or operational efficiency.
When everyone understands the goal, it becomes easier to choose the right approach and avoid wasted effort.
Agencies should clarify:
- What business metric needs improvement
- What specific workflow or decision AI will support
- How success will be measured
- What constraints or dependencies exist
- Which teams benefit from the solution
Stakeholder Alignment (Getting Everyone on the Same Page)
Effective AI implementation for clients requires alignment across marketing, IT, data, product, and leadership. Each team has different priorities, so alignment ensures everyone understands the objective, their responsibilities, and how the AI solution will affect workflows.
Agencies should confirm:
- Who is involved (stakeholder map)
- What each team contributes (data, approvals, validation)
- Who owns what (using a simple RACI model)
- What challenges or concerns exist
- How progress and decisions will be communicated
Use-Case Prioritization (Choosing What to Build First)
With many potential AI ideas, prioritization helps clients invest in solutions that deliver impact quickly. A value–complexity matrix makes it easier to identify quick wins, avoid low-impact efforts, and reserve resources for high-value strategic projects.
Agencies should guide clients by evaluating:
- Business value of each use case
- Technical complexity and integrations required
- Data availability and readiness
- Stakeholder urgency and dependencies
- Expected time to deliver visible impact
PHASE 2: Data & Infrastructure Preparation
Once goals are set, the next focus is ensuring the data and technology foundation is strong enough to support AI reliably.
Data Readiness (Ensuring the Inputs Are Reliable)
AI systems rely on accurate, complete, and accessible data. If data is inconsistent or fragmented, the model’s results will be unreliable. Assessing data readiness early prevents major delays and reduces rework during development.
Agencies should review:
- Whether essential data exists and is easy to access
- Completeness of key fields and historical records
- Consistency across platforms and tools
- Accuracy and cleanliness of the data
- Privacy or compliance limitations
Common Data Issues (Patterns That Slow Down AI Projects)
Most organizations face predictable data challenges that disrupt AI workflows. Addressing these early strengthens model accuracy and speeds up implementation.
Common problems include:
- Duplicate or inconsistent customer records
- Mismatched schemas across systems
- Missing or outdated values
- Conflicting naming conventions
- Limited access to APIs or exports
Minimum Viable Data (Starting with What’s Essential)
AI doesn’t require perfect data to begin — only the critical fields needed to support the use case. Starting with a minimum viable dataset keeps projects moving while long-term data improvements continue in the background.
Agencies should identify:
- The must-have fields for the model
- Which optional fields improve performance but aren’t required
- Any missing data that needs short-term workarounds
- What accuracy level is acceptable initially
- How often the data must be updated
Data Quality Improvement (Making Data Fit for AI)
Once gaps are identified, agencies should help refine the data to ensure it supports reliable predictions. These improvements don’t require deep engineering but dramatically enhance model quality.
Key improvements include:
- Standardizing formats and categories
- Removing duplicates and fixing outdated records
- Aligning timestamps and identifiers
- Normalizing inconsistent values
- Adding basic checks and validation rules
Infrastructure Readiness (Preparing the Technical Foundation)
AI needs a stable and scalable environment to run effectively. Setting up essential infrastructure early prevents bottlenecks during deployment and ensures models perform consistently under real-world loads.
Recommended components include:
- Scalable cloud hosting (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- Centralized data storage or warehouse
- Simple data ingestion or ETL pipelines
- Secure access controls and permissions
- Monitoring and logging for performance visibility

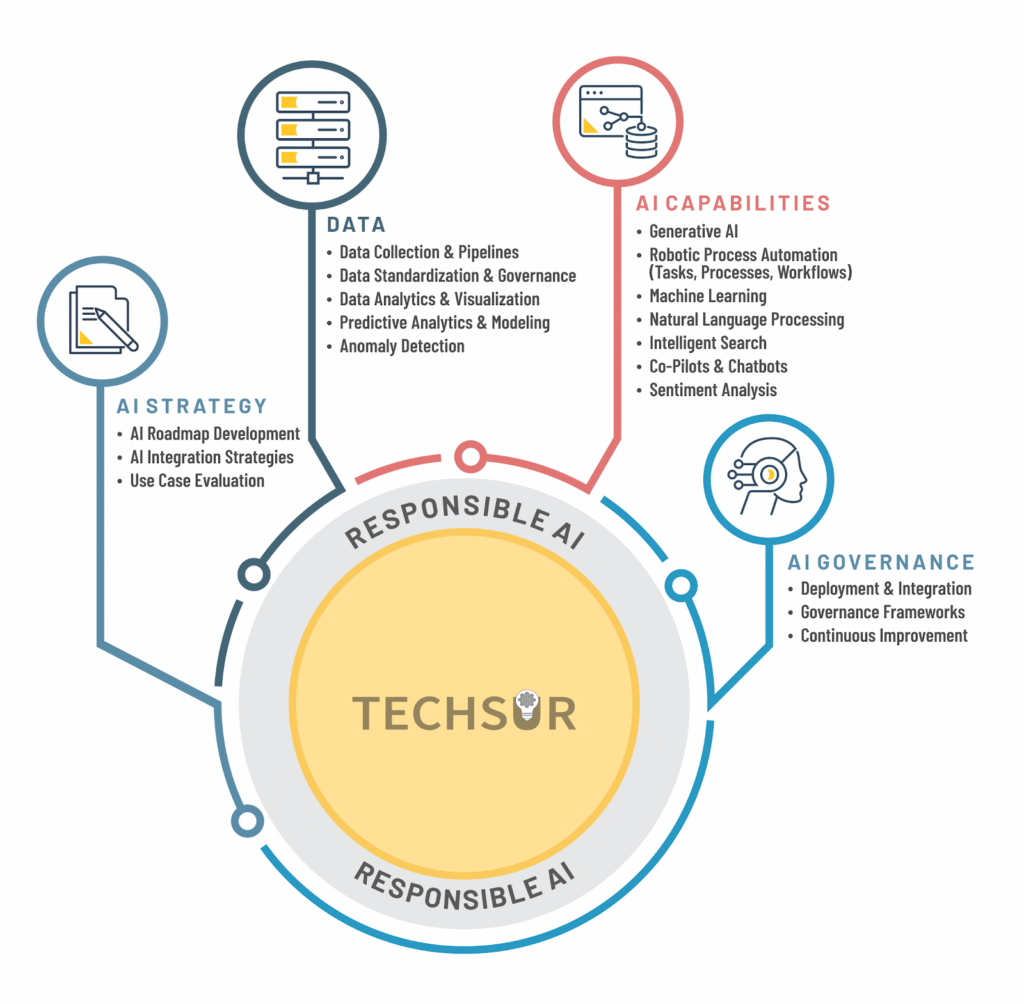
PHASE 3: Design, Architecture & Deployment
This phase transforms your defined strategy and prepared data into a working AI solution integrated with real client workflows.
Modular Architecture (Building Systems That Are Easy to Evolve)
A modular architecture breaks the AI solution into logical components that can be updated independently. This approach simplifies maintenance, reduces downtime, and supports faster experimentation and scaling.
Core components usually include:
- Data ingestion and processing layer
- Model training pipeline
- Inference or serving system
- API or integration layer
- Monitoring and observability tools
Workflow Design (Ensuring AI Fits the Way Teams Work)
AI only creates value when it integrates naturally into the client’s existing workflows. Mapping how users receive and act on AI outputs ensures the solution supports decision-making rather than disrupting it.
Agencies should define:
- Where AI outputs appear (CRM, dashboard, campaign tool)
- Who uses them and at what stage
- How decisions change when AI is added
- What happens when predictions are unclear or incorrect
- How workflows evolve over time as the model improves
Integration Points (Connecting AI to the Client’s Tools)
Most AI solutions must interact with existing platforms like CRM systems, analytics tools, or marketing automation software. Identifying integration points early ensures smooth data flow and seamless user experience.
Agencies should determine:
- What systems require two-way communication
- Which APIs or data exports are available
- How frequently data must sync
- What fallback options exist if systems fail
- Who owns each integration on the client side
Deployment Strategy (Rolling Out AI Safely and Confidently)
Deploying AI gradually reduces risk and gives teams time to validate performance. A staged or canary rollout allows small groups to test the system before it reaches all users.
A safe rollout includes:
- Internal testing with sample data
- Releasing to a small user segment first
- Monitoring early performance closely
- Expanding usage in stages
- Providing fast channels for user feedback
PHASE 4: Optimization & Continuous Improvement
Once deployed, AI requires consistent monitoring and refinement to remain accurate and effective.
Monitoring AI Performance (Tracking How the Model Behaves Over Time)
AI models naturally degrade as behaviors and markets change. Regular monitoring helps identify when the model begins drifting or returning less accurate results.
Monitoring should include:
- Accuracy and confidence scores
- Latency and response times
- Data drift or unusual patterns
- Error rates and exceptions
- Real-world outcome alignment
Feedback Loops (Using Human Input to Improve the AI)
Human feedback helps models evolve and stay relevant. Encouraging teams to review AI outputs and flag concerns enables continuous improvement and prevents blind spots.
Effective feedback loops capture:
- Incorrect or low-quality predictions
- Edge cases the model didn’t anticipate
- User suggestions or improvements
- Missed opportunities or inaccurate classifications
- Situations requiring manual overrides
Retraining Cycles (Keeping the Model Fresh and Accurate)
Models need periodic updates to reflect new behaviors and market conditions. Structured retraining cycles ensure the AI remains aligned with real-world data.
Retraining should consider:
- How often new data becomes available
- Whether drift has occurred
- Changes in customer patterns
- Product or pricing updates
- New business goals or constraints
PHASE 5 — Governance, Risk & Adoption
Governance ensures that the AI remains ethical, compliant, and well-managed — and that users trust and adopt the system.
Governance Frameworks (Creating Structure and Accountability)
Governance provides clarity around how the AI operates and who manages it. Well-defined roles and approval processes prevent confusion and ensure consistent oversight.
Governance frameworks cover:
- Ownership of the model and data
- Standards for documentation
- Approval workflows for updates
- Access and permission rules
- Compliance and audit requirements
Risk Management (Avoiding Common AI Pitfalls)
AI introduces risks that can impact accuracy, compliance, or user trust. Identifying these risks early helps agencies build safeguards into the system.
Key risks include:
- Incorrect or biased data
- Model drift over time
- Compliance requirements (GDPR, CCPA)
- Integration failures
- Misuse or misinterpretation of AI output
User Adoption (Ensuring Teams Use and Trust the AI)
The success of an AI solution depends on whether users adopt it. Providing clear guidance, simple interfaces, and visible value helps teams trust and integrate AI into daily work.
To support adoption, agencies should:
- Provide training and short demos
- Communicate value in simple terms
- Offer documentation and user guides
- Collect early feedback to refine the experience
- Show measurable wins to build confidence
PHASE 6: Client Enablement & Long-Term Success
After an agency’s AI solution is deployed, the final step is ensuring the client can use, maintain, and evolve the system confidently. This phase turns a successful implementation into long-term organizational capability.
AI is only truly valuable when teams understand how to use it—and continue getting value from it as their business changes.
Agencies should support clients by offering:
- Training and onboarding for marketing, sales, and operations teams
- Clear documentation for workflows, integrations, and troubleshooting
- Performance dashboards showing accuracy, usage, and key business outcomes
- Post-launch support windows for rapid fixes and adjustments
- Recommendations for next steps such as additional use cases, integrations, or data improvements
This phase reinforces trust, increases adoption, and naturally leads to longer-term partnerships and ongoing AI roadmap development.
FAQ
What are the key phases in an AI implementation for clients roadmap for marketing agencies?
The roadmap covers six core phases: defining objectives, aligning stakeholders, preparing data and infrastructure, designing and integrating the solution, deploying it safely, and supporting long-term improvement. Each step ensures the AI solution is purposeful, reliable, and able to scale across the client’s operations.
How does aligning AI initiatives with business objectives improve deployment success?
When AI is tied to clear business goals, it becomes easier to measure impact, prioritize features, and keep teams aligned. This prevents wasted effort and ensures the solution improves specific KPIs instead of becoming a disconnected experiment.
How does data readiness influence early-stage AI planning?
Data readiness determines whether the AI can produce reliable results. Clean, complete, and accessible data helps teams assess feasibility early and prevents delays caused by missing fields, siloed systems, or inconsistent records.
How can agencies encourage cross-department collaboration during AI projects?
Collaboration improves when roles are clearly defined and all teams understand their responsibilities. Short alignment workshops, shared documentation, and ongoing check-ins help ensure marketing, IT, data, and leadership stay coordinated throughout the project.
What are the best practices for scaling AI solutions after deployment?
Scale gradually using phased rollouts, monitor performance closely, and retrain models as data changes. Clear governance, compliance checks, and good communication across teams help the AI expand safely and continue delivering value as usage grows.
Conclusion
AI success doesn’t come from advanced models—it comes from clarity, structure, and disciplined execution. When agencies follow this roadmap, they transform AI from a buzzword into a reliable business tool that improves decisions, enhances customer experiences, and drives measurable ROI.
From discovery to deployment—and now ongoing enablement—each phase builds toward a scalable, sustainable AI capability. Agencies using this framework can confidently guide clients through the complexities of AI and deliver solutions that work today and keep improving tomorrow.
If done right, AI becomes not just a project, but a long-term advantage.
Want to go even deeper? Once you understand the implementation roadmap, the next step is choosing the right tools.
Read the companion guide: Choosing an AI-Ready Software Solution: 2025 Checklist to learn how to evaluate platforms that can actually support your roadmap.