TL;DR
Connect MCP to your chatbot by enabling the Hosted MCP Server in your CustomGPT.ai dashboard to retrieve your secure URL and token. Simply paste these credentials into any MCP-aware client, like ChatGPT or Claude Desktop, to instantly authorize your assistant to access your agent’s specific tools and knowledge base without complex integration code. Scope: Last updated: January 2026. Applies globally; align chatbot and MCP data access with local privacy laws such as GDPR in the EU and CCPA/CPRA in California.What MCP is and how it connects to chatbots
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard that lets AI applications, such as chatbots, connect to external tools, data sources, and workflows over a common “port.” Think of it as a universal way for models to talk to APIs, databases, file systems, and more, without custom integrations per tool. MCP uses a client–server model. Your chatbot (or AI assistant host, like ChatGPT) runs an MCP client. That client connects to one or more MCP servers. Each server exposes tools, resources, and prompts that the chatbot can discover and call dynamically during a conversation. When your chatbot is MCP-enabled, it can:- List tools exposed by the server (for example, “search_kb”, “create_ticket”).
- Request additional context from resources like knowledge-base documents.
- Execute actions by invoking tools, with arguments encoded in JSON-RPC.
Common ways to connect MCP to a chatbot
There are two main patterns for connecting MCP to your chatbot:1. Using built-in MCP support in AI assistants
Some platforms, like ChatGPT, include built-in UI for adding remote MCP servers via “connectors.” You paste the MCP server URL and, where required, an auth token. The platform then discovers tools from that server and surfaces them as actions the model can call. Typical flow:- Open the AI assistant’s settings.
- Find the MCP / connectors / tools section.
- Add a new MCP server and paste the URL.
- Provide any token or credentials required.
- Enable the tools for the assistant or specific workspace.
2. Using a custom MCP client or agent SDK
If you’re building your own chatbot, you can use an MCP-aware SDK, like the OpenAI Agents SDK, to connect programmatically to a remote MCP server. At a high level:- Instantiate an MCP client in your code.
- Configure it with the MCP server’s URL and authentication.
- Use the SDK to list tools and resources from that server.
- Wire tool calls into your chatbot’s reasoning loop (for example, using OpenAI’s Responses API with hosted MCP tools).
- Surface results back to the end user as messages or actions.
What you need before connecting
Before you configure the connection, ensure you have the necessary components ready on both the client and server sides. Since CustomGPT.ai handles the server infrastructure, your requirements are minimal:- A CustomGPT.ai Project (The Server): You need an active project populated with data (documents, sitemaps, or FAQs). This acts as the “brain” your chatbot will query.
- An MCP-Aware Client (The Interface): This is the application you interact with. Common options include:
- Claude Desktop App: Ensure you have the latest version installed on your local machine.
- ChatGPT: You typically need a Plus, Team, or Enterprise plan to access advanced data connectors.
- Agentic IDEs: Tools like Cursor or Windsurf if you are integrating into a coding workflow.
- Configuration Access:
- For Claude/Local Clients: You must be comfortable locating and editing JSON configuration files (specifically claude_desktop_config.json) on your computer.
How to do it with CustomGPT.ai
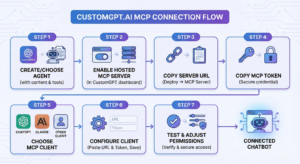
7-step setup overview
- Create or choose a CustomGPT.ai agent that has the content and tools you want your chatbot to use.
- Enable or locate the Hosted MCP Server for that project in the CustomGPT dashboard.
- Copy the MCP server URL from the “Deploy → MCP Server” section.
- Copy the MCP token from the same page, this secures your server.
- Choose an MCP client (ChatGPT connectors, Claude Desktop, or another MCP-capable tool).
- Configure the client with the URL and token, then save.
- Test and adjust MCP permissions so your chatbot only gets the access you intend.
Prepare your CustomGPT.ai agent and Hosted MCP server
Start by creating or selecting the CustomGPT.ai agent whose knowledge and tools you want your chatbot to use. That agent can be connected to docs, sites, or other content as usual. In the project, go to the Deploy section and open MCP Server. CustomGPT.ai provides a Hosted MCP Server for each project so external AI systems can connect via a secure, permission-controlled interface. Confirm that:- The MCP server is enabled for your project.
- The project has the documents and tools you expect (for example, your knowledge base or custom actions).
Get your CustomGPT MCP server URL and token
On the same Deploy → MCP Server page, you’ll see the Server URL and a way to obtain your MCP token.- The server URL typically looks like: https://mcp.customgpt.ai/projects/<project-id>/sse?token=..
- The token is fetched from the CustomGPT app under Project → Deploy → MCP Server.
- Don’t hard-code it in public repos.
- Use environment variables or secrets managers in production.
Connect your chatbot or MCP client (ChatGPT, Claude, or other tools) to CustomGPT.ai
Now plug those values into your chosen MCP-aware client. The specifics vary slightly, but the pattern is the same. With ChatGPT connectors- Open Settings → Connectors in ChatGPT.
- Click Create and choose the option to add an MCP server.
- Paste the CustomGPT MCP Server URL into the “MCP Server URL” field.
- Provide the MCP token when prompted.
- Save the connector and enable it for the assistant you’re using.
- In the client’s MCP configuration, add a new MCP server.
- Paste the CustomGPT server URL.
- Configure authentication with your CustomGPT MCP token.
- Save the configuration and restart or reload the client if required.
Test and secure the MCP connection
Once connected, you should:- Open your chatbot or MCP client and start a test conversation.
- Ask a question that clearly targets your CustomGPT knowledge (for example, “Answer from my CustomGPT knowledge base: …”).
- Confirm that the response is grounded in your project’s documents, not general web knowledge.
- In the CustomGPT dashboard, open MCP server permissions and review what external AI systems are allowed to do (read documents, run tools, etc.).
- Disable any permissions you don’t need to enforce least-privilege access.
Example: customer-support chatbot using MCP
Imagine you already have a CustomGPT.ai agent trained on your support docs, FAQs, and internal runbooks. You want a separate chatbot in ChatGPT to answer customer questions using that content, without copying all the data again. You deploy your CustomGPT agent as an MCP server and copy its MCP URL and token. In ChatGPT, you add a new connector using that URL and token. Now, when a user asks, “How do I reset my password? Answer from our support knowledge base,” ChatGPT calls the CustomGPT MCP server behind the scenes. The server fetches the right article, the model generates an answer grounded in that document, and the user sees a clear, accurate response, powered by your CustomGPT agent but delivered through your ChatGPT-based chatbot. The same pattern works with Claude Desktop or any MCP-compatible tool: one MCP server, many chatbots reusing the same knowledge and tools.Conclusion
Connecting powerful tools to your assistant shouldn’t force you to choose between brittle custom code and generic, one-size-fits-all chatbots. customgpt.ai bridges that gap with hosted MCP servers, secure permissions, and instantly reusable agents that plug into ChatGPT, Claude, or any MCP client without the integration headaches. If you’re ready to turn scattered systems into one intelligent, controllable assistant layer, get started with CustomGPT.ai and connect MCP to your chatbot today.FAQ’s
How do I connect MCP to my chatbot using CustomGPT.ai?
To connect MCP to your chatbot with CustomGPT.ai, first enable the Hosted MCP Server for your project and copy the server URL and token from the Deploy → MCP Server page. Then paste these into an MCP-aware client like ChatGPT or Claude, save the configuration, and test that your chatbot is calling CustomGPT tools and knowledge, not generic web data.Can I use one MCP server to power multiple chatbots?
Yes, a single CustomGPT.ai Hosted MCP Server can power multiple MCP-enabled chatbots or AI assistants. You simply reuse the same MCP server URL and token across compatible clients. Each chatbot can then call the same tools and knowledge base, while you centrally manage access through CustomGPT’s MCP server permissions.Frequently Asked Questions
Do the systems I want to connect need to be MCP-compliant first?
Not necessarily. Your chatbot needs to use an MCP-aware client, and that client connects to an MCP server. The MCP server can expose tools that interact with APIs, databases, file systems, and other external systems through a standard interface.
Can I connect MCP to an e-commerce backend so my chatbot can retrieve order information?
Yes, if your e-commerce system is exposed through tools on an MCP server. MCP is designed to let AI assistants connect to external tools and APIs through a common protocol, so order lookup can be implemented as a tool your chatbot is allowed to call.
What do I need to configure in Claude to connect it to MCP?
Use Claude as an MCP-aware client and provide the MCP server credentials: the secure server URL and token. Once those are entered correctly, Claude can connect to the exposed tools on that server.
Can I run MCP with a custom chatbot client or SDK instead of ChatGPT or Claude?
Yes. Any MCP-aware client can connect, including a custom agent SDK implementation. The key requirement is that your client can connect to a compatible MCP server and authenticate with the required credentials.
Can an MCP-connected chatbot access external tools and workflows?
Yes. MCP is built for that purpose: it allows chatbot clients to access tools, data sources, and workflows exposed by MCP servers using a consistent protocol.
Why connect ChatGPT or Claude through an MCP server instead of building one-off direct integrations?
MCP gives you a common integration standard, so MCP-aware clients can connect through the same protocol instead of requiring separate custom integration logic per tool connection.