Most underperforming websites are not visibly broken. Pages load correctly, traffic arrives, and analytics dashboards appear healthy.
Yet revenue stalls or grows more slowly than expected. In these situations, teams often focus on acquisition, redesigns, or incremental CRO work.
Sales raises concerns about lead quality, while marketing points to traffic volume. The underlying issue, however, is usually not any single function.
It is the conversion system as a whole. Website failures tend to occur in small, unremarkable moments: hesitation on pricing, uncertainty about fit, or unanswered questions introduced by policy or product detail.
Individually, these moments appear minor. Collectively, they determine whether intent converts into revenue. Revenue agents emerged to address this specific gap.
Rather than treating the website as a static funnel and chat as reactive support, they operate inside decision moments—when intent still exists but confidence begins to weaken.
How Revenue Agents Change Website Performance Dynamics
In early 2024, a mid-market SaaS firm observed an unusual pattern after deploying an AI-powered “revenue agent” to a limited set of product pages. Even as overall site traffic declined, form-start rates increased sharply.
No changes were made to pricing, copy, or ad spend. The primary difference was the replacement of a rules-based chatbot with an agent designed to treat each visit as a sales conversation rather than a support interaction.
Unlike traditional chat widgets, revenue agents are optimized around qualification, objection handling, and routing visitors toward high-intent actions.
They track micro-conversions, adapt responses based on behavioral signals, and log structured outcomes directly into CRM systems. This positioning shifts the role of on-site AI from reactive assistance to active revenue contribution.
Common Causes of Website Underperformance
Website underperformance rarely stems from a single broken element. Instead, conversion loss usually emerges from small points of friction that accumulate across a session.
Minor delays, unclear next steps, and unresolved doubts compound until visitors disengage. Three systems often misfire together:
- Perception: how fast and responsive the interface feels
- Orientation: how clearly the next action is signaled
- Validation: how quickly uncertainty or objections are resolved
Google’s UX research on “perceived performance” showed that once delays creep past about 3 seconds, abandonment spikes, even when content quality is high. A useful diagnostic approach is to evaluate friction density at each step of a journey.
Rather than scoring pages on visual quality, teams can assess friction across time cost, cognitive load, and emotional risk. Pages with high combined friction per required action tend to underperform, even if they appear well-designed.
In practice, improvements often come from reducing complexity rather than adding features. Simplifying comparisons, clarifying recommended options, or resolving common objections earlier in the journey can lift conversions without increasing traffic.
Revenue agents function as real-time friction auditors. By engaging visitors at moments of hesitation, they surface and offset issues that traditional analytics often miss.
The Financial Implications of Low Conversion Rates
Small changes in conversion rates often mask their true financial impact. A one-point drop rarely shows up as a dramatic traffic shift, but it compounds across acquisition, pipeline, and lifetime value. When funnels under-convert, three effects typically follow:
- Inflated acquisition costs: higher spend is required to maintain volume
- Pipeline compression: fewer qualified opportunities per session
- LTV erosion: fewer customers to amortize fixed costs
Modeling conversion deltas directly into unit economics makes this visible. For a site with 50,000 monthly visitors, a modest change in conversion rate can swing booked revenue by tens of thousands of dollars per month.
These losses often remain hidden because traffic and top-line metrics appear stable. Revenue agents change this dynamic by treating each session as a recoverable asset.
Rather than accepting bounce behavior as a binary loss, they capture intent mid-journey through assisted actions such as email capture, trial initiation, or guided booking. This reframes conversion optimization from cosmetic improvement to margin protection.
Diagnosing Website Failures: Tools and Techniques
Revenue agents depend on accurate diagnostics. One persistent issue is incomplete funnel instrumentation. Many teams track only headline events such as form submissions or purchases, leaving micro-events unmeasured. Critical signals often missing include:
- Field focus and error states
- Scroll depth and re-reading behavior
- Hesitation near pricing or policy elements
Without these signals, teams misattribute drop-off causes and default to traffic growth as a solution. Behavioral analytics combined with qualitative tools such as session replays and user testing provide a more complete picture.
When these inputs are unified, revenue agents can adapt in real time.
Why revenue agents change the calculus
- Treat every session as a recoverable asset, not a binary win or loss
- Capture intent mid-journey and convert “would-have-bounced” visitors into micro-conversions (email captures, trial starts, assisted bookings)
- Recycle otherwise lost spend into pipeline, reframing conversion work as direct margin protection
Leveraging Analytics and User Research
Effective intervention requires connecting event data to decision moments, not just page views. Revenue agents rely on signals such as hesitation, repeated interactions, and prior context to determine what to say next.
If those aren’t measured and interpreted correctly, the agent is essentially blind—no matter how advanced the model is. A practical diagnostic model consists of three layers:
- Instrumentation: defining meaningful events across the journey
- Interpretation: correlating events with qualitative insight
- Intervention: using those correlations to guide agent behavior
When these layers are aligned, agents can intervene with precision. For example, repeated pauses on a comparison section can trigger a clarifying prompt instead of a generic greeting. The challenge is not excessive data, but unclear decision rules.
Without explicit logic governing when and how an agent should act, even sophisticated models become reactive or noisy.
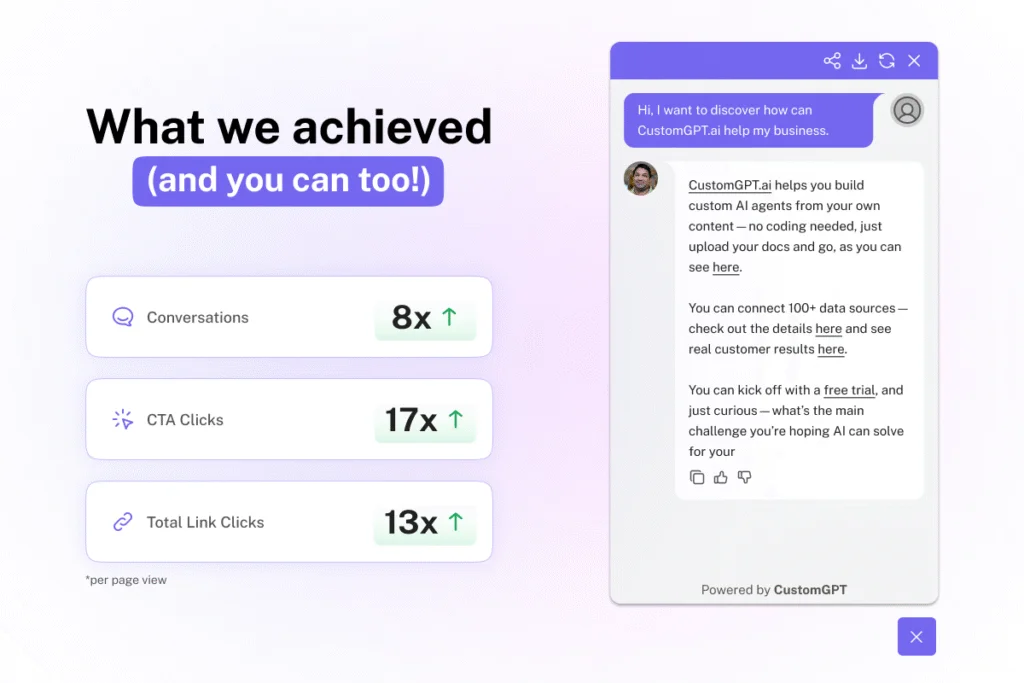
With CustomGPT.ai, you can centralize product docs, helpdesk history, sales playbooks, and research findings, then have a revenue agent that not only answers questions with high accuracy
But also adapts those answers based on the friction signals you’ve instrumented—whether your goal is deflecting Zendesk tickets, speeding up HubSpot onboarding, or turning more high‑intent visitors into actual customers.
Identifying Conversion Killers Through Heatmaps and Feedback
Heatmaps and feedback reveal that many “design issues” are actually decision breakdowns at specific moments. Three layers usually surface when you read heatmaps with feedback side by side:
- Attention anomalies: users fixating on non-interactive areas
- Interaction conflicts: rage clicks, hover-without-click, scroll reversals
- Confidence collapses: sudden exits after seeing price, forms, or policies
For revenue agents, this labeling is essential. Knowing where users stall is insufficient; agents must understand why. Once objections are cataloged and tied to page states, agents can intervene with targeted reassurance or guidance rather than generic prompts.
A reliable pattern emerges when heatmaps and feedback are analyzed together: what looks like a “design miss” is often a decision breakdown happening at a very specific micro-moment.
This matters because revenue agents don’t just need to know where people stall; they need a labeled catalogue of why those stalls occur so they can intervene with the right message or offer instead of generic reassurance.
Addressing UX Friction Points
A useful diagnostic separates page friction from dialogue friction. Some journeys suffer from silent struggle, where users hesitate but never ask for help. Others fall into a chatterbox trap, where agents over-explain simple paths.
Identifying these patterns allows teams to redesign conversations with intention rather than volume. Conversational timing often creates more friction than visual design. Poorly timed prompts, redundant questions, or shallow responses drain cognitive budget and disrupt decision-making.
They quietly drain the attention that should be spent deciding, not debugging the interface. Three dynamics govern conversational friction:
- Synchronization: when the agent intervenes
- State continuity: whether context is retained across steps
- Resolution depth: whether objections are actually closed
Get the first wrong and you create interruption; get the second wrong and you create redundancy; get the third wrong and you create shallow reassurance instead of real progress.
Measuring latency between hesitation and intervention, response time, and number of clarification turns helps teams tune agent behavior. Different verticals tolerate different levels of depth and delay, but the goal remains consistent: reduce effort required to reach a decision.
Building Trust and Authority with Visitors
Trust emerges from consistency rather than cleverness. Trust with revenue agents is built less on what they say and more on how consistently their answers line up with the rest of your system.
Revenue agents must align with existing copy, pricing, policies, and support history.
That matters because visitors subconsciously compare every answer against prior expectations; one mismatch in tone, policy, or detail can downgrade the entire experience from “advisor” to “scripted bot.” Three mechanisms underpin trust:
- Source coherence: the agent draws from the same canonical knowledge you use internally
- Policy fidelity: it never contradicts legal, pricing, or support rules
- Narrative continuity: it remembers and reuses user context across the session
Operationalizing trust requires auditing agent responses against internal documentation and user feedback. Over-personalization or excessive behavioral references can backfire, especially in regulated or privacy-sensitive contexts.
Centralizing product documentation, contracts, and support macros ensures that agents speak with one coherent voice from first interaction to conversion.
Integrating Revenue Metrics into Website Design
A revenue agent only becomes truly effective when page layouts are engineered around a single construct: Revenue Event Density—how much qualified economic value a page can generate per 100 visits, not how many generic clicks it produces.
This matters because sales teams care about opportunity value, not UX micro-wins. Metrics such as pipeline value per session or qualified leads per visit align design decisions with economic outcomes. This requires three elements:
- Instrumentation: economic weights for actions (pricing views, calculators, agent-led qualification)
- Layout logic: elements placed in proportion to expected revenue contribution
- Agent orchestration: nudging toward high-value actions instead of answering passively
When interactive elements are evaluated based on expected revenue contribution and friction cost, layout debates shift from aesthetics to outcomes. Agents can then route visitors along paths that balance value and effort in real time.
Ensuring Consistency Between Messaging and Sales Goals
The real constraint isn’t “having the right message,” it’s keeping every message synchronized with where a visitor sits in your sales process and what your revenue team is actually optimizing for.
That matters because most sites still treat copy, CTAs, and chatbot scripts as static assets, while sales teams work from live playbooks, evolving qualifiers, and updated offers.
The gap between those two systems is where you quietly lose deals: a revenue agent promotes a free trial when SDRs are comped on booked demos, or reassures on price when the real blocker is procurement risk. An effective alignment loop includes:
- Intent mapping: every page and agent entry point is tagged to a funnel stage and target sales outcome.
- Playbook binding: the agent pulls objections, discovery questions, and CTAs directly from your sales enablement content.
- Constraint rules: guardrails encode what not to say for each segment or stage.
- Feedback ingestion: win/loss notes and CRM outcomes tune future dialog choices.
When this loop is automated, agents reinforce real sales objectives instead of improvising around disconnected marketing narratives.
Continuous Testing and Improvement for Sustained Success
Revenue agents degrade when their behavior freezes. High-performing teams treat each conversation as an experiment with a measurable outcome. Testing should extend beyond copy to include:
- Trigger timing and thresholds
- Qualification depth
- Objective functions tied to downstream quality
Logging variant IDs alongside CRM outcomes allows teams to optimize for durable revenue rather than superficial engagement. Markets shift, and messaging that once worked can underperform as buyer behavior changes. Continuous testing ensures agents adapt in lockstep with pipeline reality.
Image source: gptexperthub.com
Implementing A/B Testing for Ongoing Optimization
The most useful experiments compare decision policies rather than widgets. Testing when an agent intervenes, how it qualifies, and what it optimizes for reveals leverage points that copy tests miss.
Organizing experiments by trigger logic, conversation strategy, and objective function prevents local optimizations that degrade lead quality. Measuring downstream acceptance, progression, and retention ensures that winning variants align with the revenue model.
Adapting to Market Changes and User Feedback
The single lever that really governs adaptation is how fast your revenue agent can translate weak behavioral signals into new conversation policies without blowing up lead quality.
This matters because market shifts rarely arrive as clean trends; they show up as tiny distortions in behavior—more price peeking, shorter sessions from a key segment, different questions in open-text fields—that your agent either reacts to or ignores. Effective adaptation requires:
- A signal layer that detects weak changes
- A policy layer that defines response options
- Governance that controls rollout and rollback
By predefining adjustment levers, teams avoid reactive improvisation. When analytics, knowledge, and agent configuration live in one system, adaptation becomes operational rather than anecdotal.
FAQ
What is a revenue agent in the context of website conversion optimization, and how does it differ from traditional chatbots and live chat workflows?
A revenue agent is an AI-driven system designed to guide visitors toward high-value outcomes using behavioral signals, qualification logic, and contextual responses. Unlike traditional chatbots, it optimizes for revenue events rather than support resolution.
How do revenue agents detect failing journeys?
They monitor behavioral signals such as hesitation, repeated interactions, and abandonment patterns, then intervene contextually to clarify objections or redirect users toward higher-intent paths.
How do they integrate with CRM and analytics tools?
Revenue agents log structured conversation data and intent signals into CRM and analytics platforms, enabling attribution between on-site interactions and downstream sales outcomes.
What metrics matter most?
Key metrics include assisted conversion rate, qualified leads per visit, pipeline value per session, and downstream win rates for agent-influenced journeys.
Conclusion
Revenue agents transform website optimization from passive measurement into active revenue recovery. By responding to friction and hesitation in real time, they convert failing sessions into qualified outcomes rather than lost traffic.
When analytics, messaging, and sales goals are aligned, the agent becomes a continuous system for protecting and increasing revenue—focusing not on more clicks, but on better decisions and higher-value conversions.
Turn Website Friction Into Revenue
Deploy revenue agents to reduce friction and convert lost intent into qualified sales.
Trusted by thousands of organizations worldwide